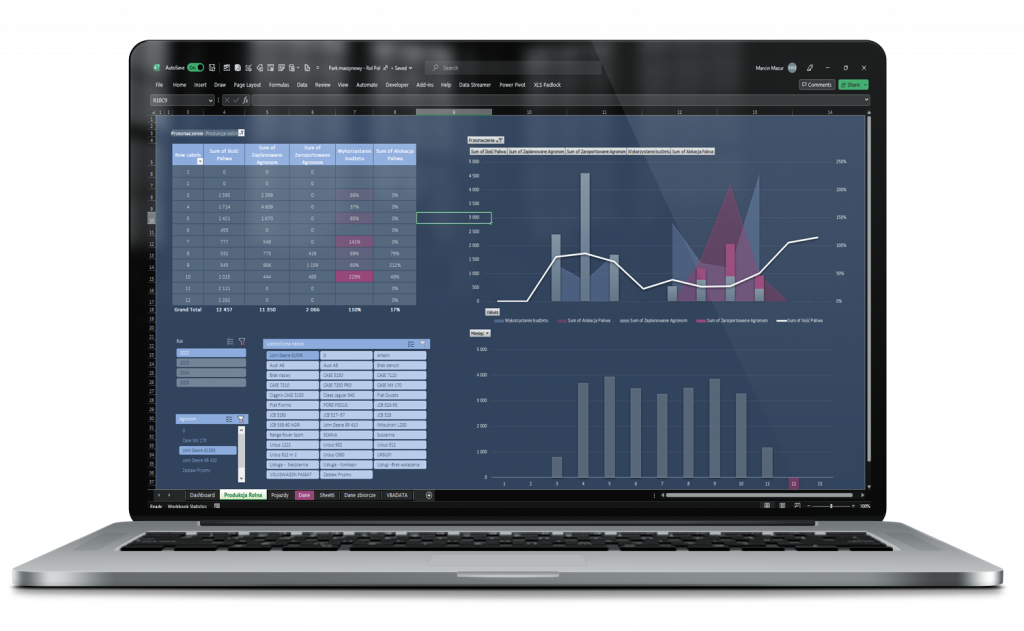
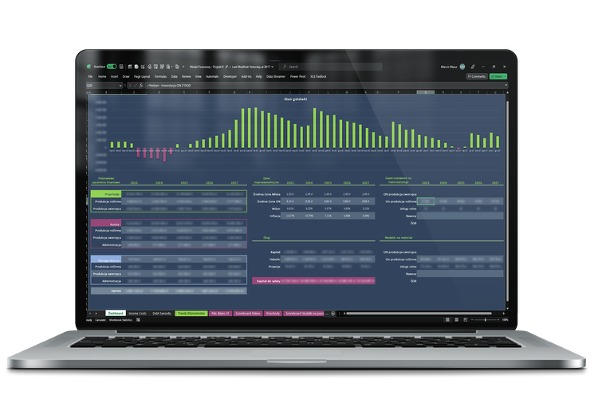
It all started with the question: how much does it really cost to produce a liter of milk?
It led to a full operational transformation and the creation of an integrated management system covering finance, technology, dynamic budgeting, production, and inventory.
The farm began to specialize in the area where it has the greatest potential – milk production.
The transformation was a response to dynamic geopolitical, climatic, and demographic changes that demanded a new management model: data-driven, resilient to shocks, and ready to collaborate with investors.
The changes involved full operational and financial integration: from aligning the crop plan for profitability (considering soil potential, subsidies, and machinery), through implementing cost and production control systems, to designing an investment roadmap and securing financing in line with the farm’s realities.